Using IoT in Healthcare to Tackle Unique Challenges

Connected devices are growing increasingly common as the technology matures. IoT in healthcare, in particular, has shown rapid growth since the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic, with the global market for IoT medical devices expected to exceed a valuation of $973.3 Billion (USD) by 2028.
There are innumerable ways in which IoT technologies have found a home in healthcare settings, from remote patient monitoring to wearable devices to track a patient’s wellbeing. Yet there are also some more interesting and unique applications out there for IoT in healthcare.
Let’s take a look at some of the less common ways connected IoT devices are helping keep the world’s population happy and healthy.

Connected Devices Help Monitor Depression and Mood
According to World Health Organization, approximately 300 million people around the world suffer from depression. It is the leading case of disability for people aged 15-44 and is estimated to account for around $23 billion in lost workdays each year, to say nothing of the mental and physical tolls it can take on the individual and those around them. Worse yet, its symptoms can be hard to track, with many medical practices being ill-equipped to monitor the condition and relying upon patients to self-report their issues.
That’s where “mood-aware” IoT devices come in. These tools analyze data from things like heart rate and blood pressure monitors to help remotely gauge a person’s mental health -or at least some of the physical symptoms associated with it. While neither our understanding of mental health disorders nor the technology to monitor and respond to their effects is fully developed, the hope is that observing behaviors associated with depression or anger can help better recognize the symptoms before they become a problem.
By utilizing AI in IoT, many of the signs of a depressive state can be identified the moment they arise. This could, in turn, trigger a number of responses to help address depressive states, whether it be as simple as changing the lighting of a room or even administering medication.
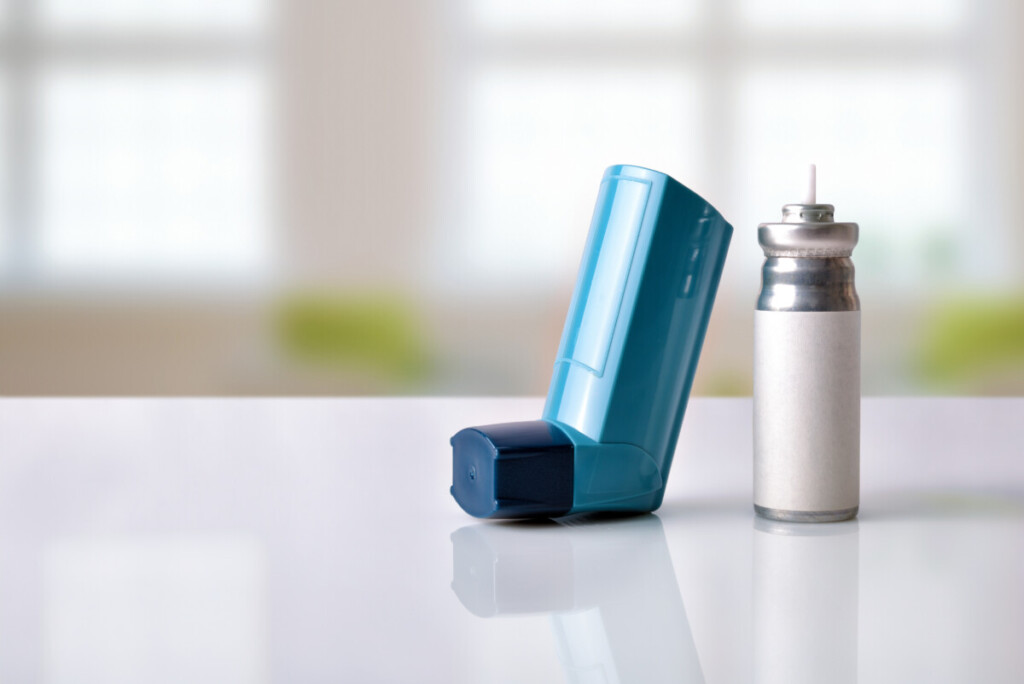

Connected Inhalers Help Treat Chronic Lung Diseases
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death in the world, yet early diagnosis and treatment can help to slow or stem many of its symptoms. Enter smart inhalers, IoT devices that can monitor the frequency of attacks, analyze atmospheric data (i.e. Air quality) for any possible triggers, and register the amount of medication dispensed during an incident.
There are many ways this information could be used to help improve the treatment or management of COPD, from improved scheduling of medication to an increased awareness of environmental triggers in a given space. This data can also be monitored by medical facilities to understand the severity of a patient’s condition so as to better prescribe a treatment schedule.
Many of these devices work by embedding sensors into the inhaler itself, often connecting to a remote monitoring center via smartphone apps and Bluetooth connectivity. Yet there are many models (predominant geared toward Asthma treatments) currently running through the FDA approval process that utilize external attachments for existing inhaler technologies.
Robotic Surgery Is The Future of IoT in Healthcare
Though IoT in healthcare can be found in everything from monitoring devices to smart pills, the application that feels the most like science fiction may be robotic surgery. This feat of medical science is accomplished by injecting microscopic internet-connected robots into a patient. These robots can then be controlled externally to perform any number of complex surgical procedures that may otherwise prove difficult for human hands.
Though this may sound far-fetched, these technologies are already being deployed in the field. The Virtual Incision Corporation recently announced the first ever in-human use of its miniature robotically assisted surgical device (RASD) to remove some cancerous growths from a patient. The RASD is administered into the body via a small incision, does not require a dedicated operating room or specialized infrastructure, and is expected to be less expensive than existing robotic medical procedures.
The successful completion of this surgery is a proof of concept that could help usher in the future of IoT in Healthcare as it pertains to minimally invasive surgical procedures.
“To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time an active miniaturized robot has performed complex surgical tasks with the robot inside a living human, which is a significant milestone in robotics and in surgery,” said Shane Farritor, Virtual Incision’s co-founder and chief technical officer.

Connectivity is Key to IoT in Healthcare
No matter the solution, no matter the application, IoT devices need safe and consistent connectivity to work. As such, healthcare organizations looking to deploy IoT solutions will want to seek out a connectivity partner with robust connectivity options and an eye toward security.
Soracom currently connects more than 4 million IoT devices across the globe and offers a bevy of security options to help keep your data out of the hands of bad actors. From private networking and authentication tools to secure provisioning and global support, you’re sure to find what you need with Soracom.
………………
Got a question for Soracom? Whether you’re an existing customer, interested in learning more about our product and services, or want to learn about our Partner program – we’d love to hear from you!



